Figures S9-S16: Static area velocity analysis for all tests
Contents
Figures S9-S16: Static area velocity analysis for all tests¶
This notebook shows the analysis of static area velocity (abbreviated as SAV in Table S2) with the supplemental figures in the bottom.
Basic information, importing modules, load data list and static-area shapefile¶
See Table S1 for all the Kaskawulsh glacier images and parameter sets used in this study.
import glaft
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
We start by loading the data list. Whichever line in the cell blow works for reproducing the figures.
../manifest.csvcontains only the parameter table (Table S1)../results_2022.csvcontains both the parameter table and all the metrics calculated (Table S2) in this study.
If you want to reproduce the workflow and the figures, make sure you have downloaded all necessary input files from https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/HE7YR and have updated the Vx and Vy columns in either csv file with the downloaded file paths before starting the analysis.
# df = pd.read_csv('../manifest.csv', dtype=str)
df = pd.read_csv('../results_2022.csv', dtype=str)
Specify static area. Change the path to the downloaded shapefile from https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/HE7YR before running the cell.
in_shp = '/home/jovyan/Projects/PX_comparison/shapefiles/bedrock_V2.shp'
Perform analysis¶
exps = {}
for idx, row in df.iterrows():
exp = glaft.Velocity(vxfile=row.Vx, vyfile=row.Vy, static_area=in_shp, kde_gridsize=60, thres_sigma=2.0)
exp.static_terrain_analysis()
exps[idx] = exp
Visualize results¶
Click to show
# Font and line width settings
font = {'size' : 13}
mpl.rc('font', **font)
axes_settings = {'linewidth' : 2}
mpl.rc('axes', **axes_settings)
def plot_batch(sub_df, zoom=False, datestr=''):
"""
Plot static area velocity distribution for all the tests from the same image pair.
"""
fig, axs = plt.subplots(8, 6, figsize=(20, 26), constrained_layout=True)
n = 0
for idx, row in sub_df.iterrows():
ax_sel = axs[n // 6, n % 6]
exp = exps[idx]
if zoom:
exp.plot_zoomed_extent(ax=ax_sel)
ax_sel.set_xlim(-1.5, 1.5)
ax_sel.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
else:
exp.plot_full_extent(ax=ax_sel)
# adjust extent
xmin, xmax = ax_sel.get_xlim()
ymin, ymax = ax_sel.get_ylim()
newmin = max(min(xmin, ymin), -10)
newmax = min(max(xmax, ymax), 10)
ax_sel.set_xlim(newmin, newmax)
ax_sel.set_ylim(newmin, newmax)
ax_sel.set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
# show incorrect match percentage
ax_sel.text(0.95, 0.95, '{:.1f}%'.format(exp.outlier_percent * 100), ha='right', va='top', transform=ax_sel.transAxes, backgroundcolor=(1, 1, 1, 0.5))
#### title label
templatesize = row['Template size (px)']
# change long GIV label "varying: multi-pass" to "multi"
templatesize = 'multi' if templatesize == 'varying: multi-pass' else templatesize
if row.Software == 'Vmap':
label = '-'.join((row.Software, templatesize, row['Pixel spacing (px)'], row.Prefilter)) + '\n' + row.Subpixel
else:
label = '-'.join((row.Software, templatesize, row['Pixel spacing (px)'], row.Prefilter))
ax_sel.set_title(label)
####
n += 1
# delete empty axes
for i in range(n, 48):
ax_sel = axs[i // 6, i % 6]
fig.delaxes(ax_sel)
# legends
fig.text(0.5, 0.06,
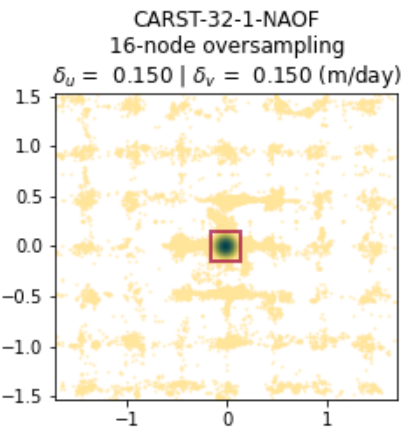
'{}\nX axis: static area $V_x$ (m/day) \nY axis: static area $V_y$ (m/day) \nPercentage: amount of incorrect matches to all matches'.format(datestr),
fontsize=16, ha='center')
return fig, axs
Click to show
### To reproduce the figures, uncomment and run the rest of this cell.
# for datestr in ['LS8-20180304-20180405', 'LS8-20180802-20180818', 'Sen2-20180304-20180314', 'Sen2-20180508-20180627']:
# sub_df = df.loc[df['Date'] == datestr]
# fig, axs = plot_batch(sub_df, zoom=False, datestr=datestr)
# fig.patch.set_facecolor('xkcd:white')
# fig.savefig('figs/{}-SAV-full.png'.format(datestr))
# fig, axs = plot_batch(sub_df, zoom=True, datestr=datestr)
# fig.patch.set_facecolor('xkcd:white')
# fig.savefig('figs/{}-SAV-zoomed.png'.format(datestr))
 Figure S9. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair
Figure S9. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair LS8-20180304-20180405 (full extent).
 Figure S10. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair
Figure S10. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair LS8-20180304-20180405 (zoomed with kernel density estimation).
 Figure S11. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair
Figure S11. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair LS8-20180802-20180818. (full extent).
 Figure S12. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair
Figure S12. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair LS8-20180802-20180818. (zoomed with kernel density estimation).
 Figure S13. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair
Figure S13. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair Sen2-20180304-20180314. (full extent).
 Figure S14. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair
Figure S14. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair Sen2-20180304-20180314. (zoomed with kernel density estimation).
 Figure S15. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair
Figure S15. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair Sen2-20180508-20180627. (full extent).
 Figure S16. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair
Figure S16. Static terrain velocity distribution of the pair Sen2-20180508-20180627. (zoomed with kernel density estimation).
Save results¶
for idx, exp in exps.items():
df.loc[idx, 'SAV-uncertainty-x'] = exp.metric_static_terrain_x
df.loc[idx, 'SAV-uncertainty-y'] = exp.metric_static_terrain_y
df.loc[idx, 'SAV-peak-x'] = exp.kdepeak_x
df.loc[idx, 'SAV-peak-y'] = exp.kdepeak_y
df.loc[idx, 'SAV-outlier-percent'] = exp.outlier_percent * 100
df.to_csv('../results_2022.csv', index=False)